Aging profile assignments:
Go to Storage Management settings > Aging profile assignments.
In this tab, you can assign or change an aging profile of a specific InfoProvider.
Archive storages:
Go to Storage Management settings > Archive storages.
If you are using SNP Outboard™ with the NLS solution, you can define the preferred storage location of the NLS database.
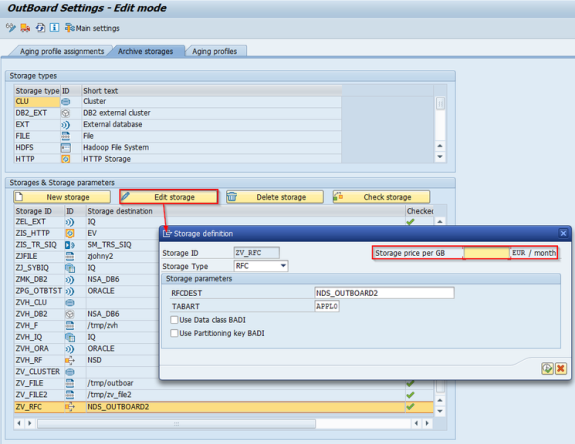
Storage definition
SNP Outboard™ Analytics can handle an additional, external database or non-SAP®-based software for data management, thus keeping the system landscape simple and easy to maintain. Use of such an external database or non-SAP®-based software is not mandatory.
You can click the Storage Type to choose the preferred storage location from the following predefined possibilities:
Cluster storage
The storage saves data in the database tables of the BW system. This solution is not supported if the primary system is running on the SAP HANA database.
RFC storage
The storage saves data in separate database tables on a remotely available system. RFC connections defined earlier can be set via transaction SM59.
File storage
The storage saves data in separate files on a file system. The file name is determined by the request and package.
Supported operating systems: Windows© Server, Unix, Linux, AIX©, HP-UX© and WebDAV. The destination path must be available for the system and the user.
External database
The storage saves data in separate database tables in a remotely available database. You must also define the secondary connection to this database (see the SAP Note 808505). The name of the connection must not contain any special characters (e.g. space).
External database MaxDB
As of with SNP Outboard™ SP20, it is possible to use the MaxDB database as external binary storage.
DB2 transparent storage
As of with SNP Outboard™ SP17, it is possible to create transparent storage for a DB2 database using a column-oriented approach. However, because data is not compressed, the compression ratio is not comparable to the non-transparent archiving when using cluster tables.
Transparent storage Sybase IQ
It is possible to create transparent storage for a Sybase IQ database.
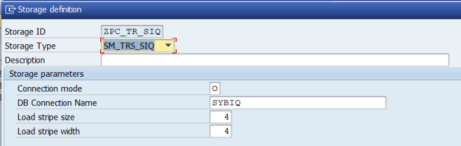
Transparent Sybase IQ – storage definition
The following options are available:
-
Connection mode: O stands for an open connection. OpenSQL is used.
-
DB connection name: Name of a database connection.
-
Load stripe size: Size of the stripe. This is a multiple of SYBASE_IQ_BUFFER_SIZE (optional).
-
Load stripe width: Number of parallel processes (optional).
Further information is available in SAP Note 2128579.
Load striping across multiple disks is an essential technique for good performance.
Disk striping can be performed at different places in the system, often as a part of RAID hardware or software.
Load striping parallelizes data inserts across multiple disk drives. In order to set up a stripe load, the database connection must be configured to support this feature.
More information about load striping support or about the setup is available in the online in the Sybase IQ support center. Alternatively, you can contact SNP Support for more information.
Oracle transparent storage
This is transparent storage for an Oracle database.

Archive storage types – Oracle
Hadoop storage
Apache Hadoop is implemented as binary storage (compressed). SNP Outboard™ for Analytics is compatible with Cloudera’s implementation of Hadoop, Hive and Impala interface components as of version CDH 5.x.
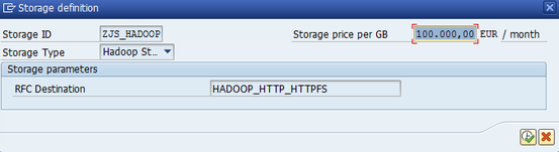
Archive storage types - Hadoop
For more details on how to connect Hadoop, contact SNP Support or ask directly for separate Hadoop and SNP Outboard™ documentation.
MSSQL BLOB storage
This enables data storage in a remote MSSQL database in a compressed BLOB structure. This reduces the amount of data that is physically stored, but it can also lead to a longer processing time in comparison to a transparent solution. Due to the limitations on the MSSQL side, the maximum size for one BLOB line is 8,000 bytes.
MSSQL transparent storage
Archiving into transparent MSSQL storage is supported in SNP Outboard™ Storage Management. Using this option, data in the archive can be accessed more quickly through transparent tables. However, the compression ratio is lower compared with archiving into cluster tables.